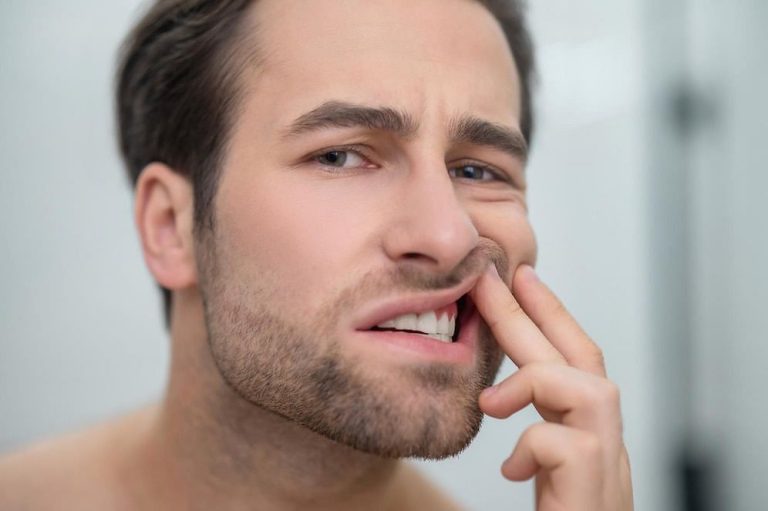
Periodontal disease, sometimes referred to as gum disease, is a widespread oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a progressive disease that, if left untreated, can lead to serious complications.
In this article, we explore the symptoms, stages and possible consequences of gum disease.
Symptoms of gingivitis

Recognizing the early signs of periodontal disease is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment.
Here are some typical symptoms to look out for:
Inflammation of the gums: Gingivitis is often first detected by swollen, red or tender gums. Healthy gums should be pink and firm.
Bleeding gums: If your gums bleed easily, especially when brushing or flossing, it may be a sign of periodontal disease. Healthy gums should not bleed.
Receding gums: As periodontal disease progresses, the gum tissue may begin to pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots of the teeth. As a result, the teeth may become more sensitive and appear longer.
Persistent bad breath: Bad breath that does not go away even after brushing and using mouthwashes can be a symptom of periodontal disease. Bad breath is caused by bacteria that accumulate in the pockets that form between the gums and teeth.
Stages of periodontal disease

Periodontal disease develops in different stages, each with its own characteristics and effects. The stages are:
Gingivitis: This is the earliest stage of periodontal disease and is characterized by gum inflammation. At this stage, the disease is reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional dental cleaning.
Early periodontitis: Gingivitis can progress to early periodontitis if left untreated. At this point, the infection has already started to damage the bone that supports the teeth, resulting in bone loss and wider gum pockets.
Moderate periodontitis: As the disease progresses, the gum pockets deepen and more bone loss occurs. Teeth can become loose or shifted, affecting the bite and overall oral health.
Advanced periodontitis: At this stage, the damage is severe and the teeth may be at risk of falling out. Extensive bone loss, gingival recession, and tooth mobility are common features.
Can gum disease kill you?


While periodontal disease itself may not directly cause death, it can have serious effects on overall health.
Research has shown a link between periodontal disease and various systemic diseases, including heart disease, stroke, diabetes and respiratory infections. Bacteria present in infected gums can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, contributing to these health problems.
Can gum disease make you sick?
Yes, gum disease can make you sick. The chronic inflammation associated with periodontal disease can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight infections.
In addition, bacteria in the mouth can cause respiratory infections when inhaled into the lungs.
Prevention and treatment
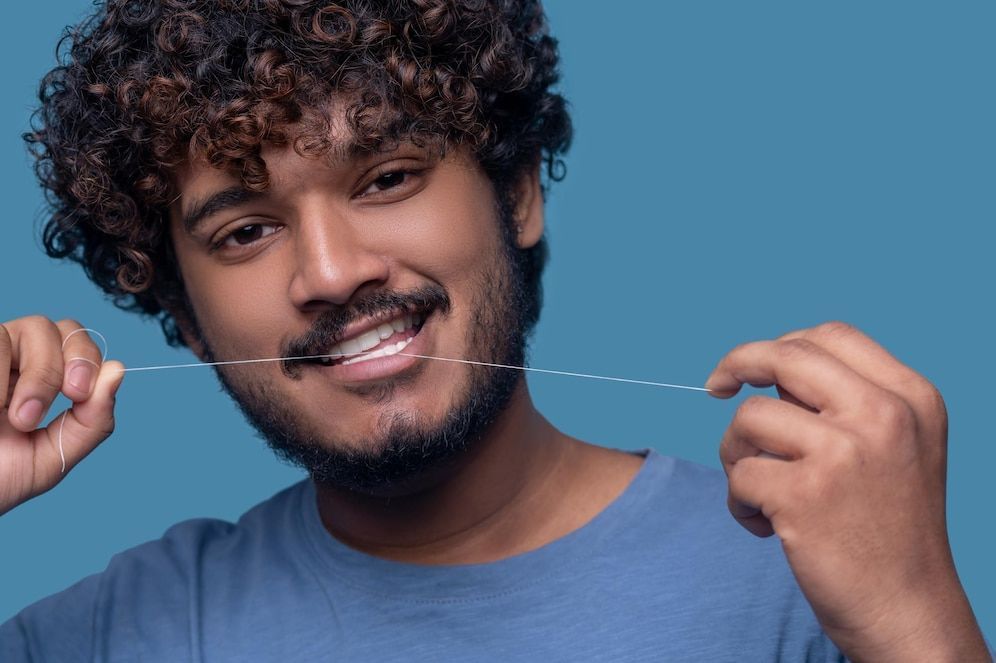


Gum disease should be avoided if one wants to keep their teeth healthy. Plaque removal and bacterial build-up can be prevented by brushing, flossing and regular professional dental cleanings.
If periodontal disease is found, treatments such as deep cleaning, antibiotics and, in severe cases, surgery may be needed to control the infection and restore oral health.
If left untreated, gum disease, a common oral health problem, can have significant effects.
In order to maintain healthy gums and overall well-being, it is essential to recognize the symptoms, understand the stages and take preventive measures. Regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene are key to avoiding periodontal disease. Remember, a healthy smile starts with healthy gums.

