Periodontitis, commonly known as gum disease, begins as a seemingly small infection, but can escalate in a serious condition that damages the soft tissue surrounding the teeth. In addition to causing pain, bad breathing and chewing difficulty, its connection to diabetes raises additional health concerns for millions of patients worldwide.
Dr. Neetu Kamra, Head of Dental and Maxillofacial Surgery at Blk-Max Super Specialty HospitalIt explains this critical relationship, “people with diabetes are more likely to have periodontal disease (gum), a gum and bones infection that hold their teeth in place.
Understanding evolution: from gingivitis to periodontitis
The gum disease is gradually developing, with each phase of increasingly serious threats to oral health. Dr. Kamra notes: “If left untreated, the disease progresses to the stages, from inflammatory gums to tooth loss.
Gingivitis marks the first stage of the gum disease, characterized by mild inflammation of the soft tissues around your teeth. This condition develops when plaque and tartar accumulate near the gum line, causing irritation and inflammation.
Without proper treatment, gingivitis can proceed with periodontitis. At this stage, the gums can retreat from the teeth, creating infected pockets. The combination of bacteria and inflammatory response to your body begins to break the bone and connective tissue that anchor your teeth. In advanced cases, teeth can be loose and possibly require export.
Don’t miss: Do you always have to pee after sex? Weighs gynecologist in
Relationship between diabetes and gum diseases
The relationship between diabetes and gum disease acts as a circular interaction where each condition can aggravate the other. “If your diabetes are not under control, you are more likely to develop problems in your mouth,” explains Dr. Kamra. “In turn, gum disease can make your blood sugar harder to control.”
This is because the increased blood sugar changes the composition of saliva, including increased glucose levels in saliva. These changes create an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to thrive, promote plaque formation and accelerate tooth decay.
The recognition of early gum disease warning signs is vital, especially for people with diabetes. Dr. Kamra advises patients to check these symptoms:
- Gums that look red, swollen or bleeding during brushing or thread
- Recede gums that are removed from teeth
- Loose teeth or growing spaces between teeth
- Persistent dry mouth (which can also be an important sign of diabetes)
- Happy Breathe Breathing that does not improve with normal brushing
Strategies to maintain oral health with diabetes
- Check your blood glucose levels. Maintaining sugar levels on target reduces risk factors for periodontal disease and improves the effects of treatment.
- Create strict oral hygiene habits. Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and thread regularly to remove the plate from the areas that the toothbrush cannot reach.
- Schedule regular dental checks. Regular professional cleaning and exams can catch problems early. “Be sure to tell your dentist that you have diabetes,” says Dr. Kamra.
- Denture problems immediately. “Tell your dentist if your dentures do not fit properly, or if your gums are painful,” Dr. Kamra advises, as bad dental devices can cause tissue damage and infection.
- Eliminate the use of tobacco. “Smoking makes gum disease worse,” warns Dr. Kamra. The use of tobacco significantly increases the risk of periodontal disease and complicates diabetes management.
- Improve the quality of your diet. “Fruits and vegetables are important for bone and dental health and help manage blood sugar levels,” notes Dr. Kamra. Nutrient -rich foods support both oral health and glycemic control.
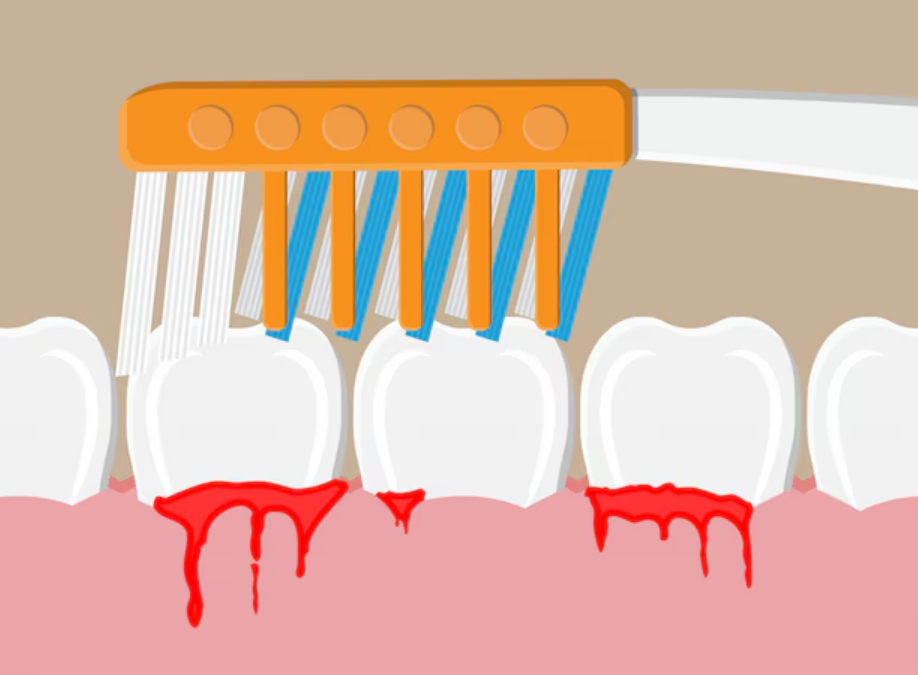
Understanding the connection between diabetes and gum disease enables patients to take precautionary measures to protect both their oral health and general well -being. By applying these recommendations and maintaining regular communication with both dental and medical providers, people with diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of developing serious periodontal diseases and its relative complications.
Don’t miss: How to brush properly and thread: 8 errors to avoid
Continue reading Herzindagi for more such stories.
Image courtesy: Freepik

