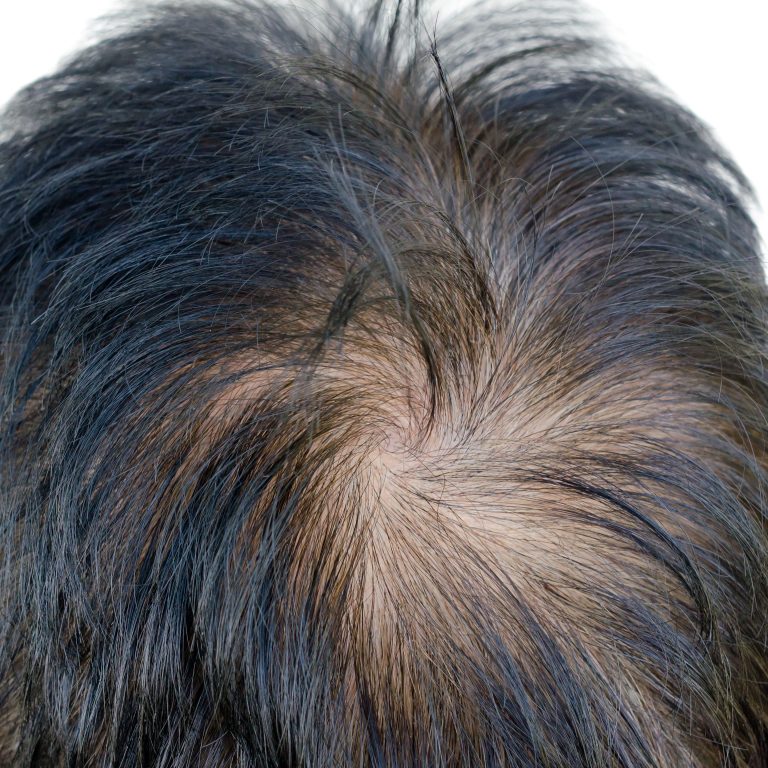
To evaluate the efficacy of minoxidil versus minoxidil combined with YAG erbium fractional ablation laser in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia, researchers conducted a randomized, parallel-group trial of 30 male patients. Study results showed that both groups showed statistically significant improvements in patient satisfaction, photography, and dermoscopy scores, although the group receiving the combination therapy had a slightly higher dermoscopy score.1
Patients with moderate to severe scalp involvement were assigned to the intervention group or the control group. The intervention group received 1 mL of 5% minoxidil topical solution 2 times a day and 6 sessions of 2940-nm YAG fractional erbium ablation laser (Handpiece type: 8 × 8 mm, pulse energy: 1500 mj/cm2, frequency: 3, pulse mode: short) at 2 week intervals.
The control group was treated with 1 mL of 5% minoxidil topical twice daily. Treatment for both groups continued for 6 months.
Treatment outcomes were assessed by photography, dermoscopy, and patient satisfaction 24 weeks after initiation of treatment. Photographs were taken at baseline and again after 6 months of treatment.
Photographs were taken in 4 vortex views and 2 dermatologists rated severity based on a 7-point scale. Dermatoscopy was performed from 3 areas of the scalp and evaluated on a 7-point scale. Patient satisfaction with treatment was also assessed on a 7-point scale.
The mean age of the participants was 33.7 ± 8 years with a mean disease duration of 12.4 ± 8 years. The 2 groups were comparable in terms of age, medical history, degree of hair loss, and duration of disease.
Both groups achieved statistically significant improvement based on photo assessments, dermoscopy and patient satisfaction. The researchers noted that, “The correlation test showed a negative correlation between disease duration and treatment response, and patients with lower Hamilton-Norwood scale scores and shorter disease duration showed better treatment responses in both groups.Pi < 0.001).'
The group receiving the combination of minoxidil and laser therapy had a higher dermoscopy score than patients receiving minoxidil alone (Pi= .016). Patient satisfaction and photography scores were comparable.
Adverse events (AEs) included pruritus of the scalp and pruritus of the scalp with seborrheic dermatitis in the group receiving minoxidil alone. In the combined treatment group, 2 patients complained of hair shaft damage, 1 experienced erythema and contact dermatitis, and 2 experienced mild burning. The number of AEs was similar between groups.
The authors concluded that both groups showed satisfactory improvement in hair conditions, but the group treated with minoxidil and laser had a slightly better outcome.
Report
- Mokhtari F, Zavare Z, Iraji F. Topical 5% minoxidil versus combined YAG erbium laser and topical 5% minoxidil in androgenetic alopecia: A randomized controlled trial. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023? 00:1-7. doi:10.1111/jocd.15955