FMX nanzors eliminate bacterial biofilm resistant to drugs associated with severe endodontic infection through catalytic activation or2THE2. Credit: Newspaper of clinical research (2024). DOI: 10.1172/JCI183576
Top periodontitis, a chronic and tough dental infection for treatment, affects more than half of the population worldwide and is the main cause of tooth loss. The root canal is the typical treatment, but existing approaches to the treatment of infection have many restrictions that can cause complications, leading to treatment failure.
Now, researchers at the School of Dental Medicine, Perelman Medical School and the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences have identified a very promising new therapeutic choice that could potentially disrupt current treatments. The team of researchers is part of the Innovation and Dentistry Center, a joint research center between Penn’s dental medicine and Penn engineering that utilizes mechanics and computational approaches to promote innovation in oral and craniofacial health care.
To one paper Published in Newspaper of clinical researchThey show that Ferumoxytol, an iron -approved FDA of iron nanoparticine, significantly reduces infection in patients diagnosed with top periodontitis.
“This is the first study showing the clinical efficacy of a nanotherapy in the treatment of a serious chronic biofilm infection,” says Hyun (Michel) Koo of Penn Dental Medicine. “We have previously found that Ferumoxytol effectively inhibits the pathogenic biofilm in the human mouth, so we asked if these same nanoparticles could deal with an even more difficult biofilm: those hiding in the radical channel.”
Biofilm are dense, sticky bacterial communities associated with surfaces and cause meaningless infections. A protective uterus and the antimicrobial resistance of the germs inhabiting them make it difficult to treat biofilm (such as dental plate). However, when they are deeply formed on the tooth root channel, they are an even greater challenge.
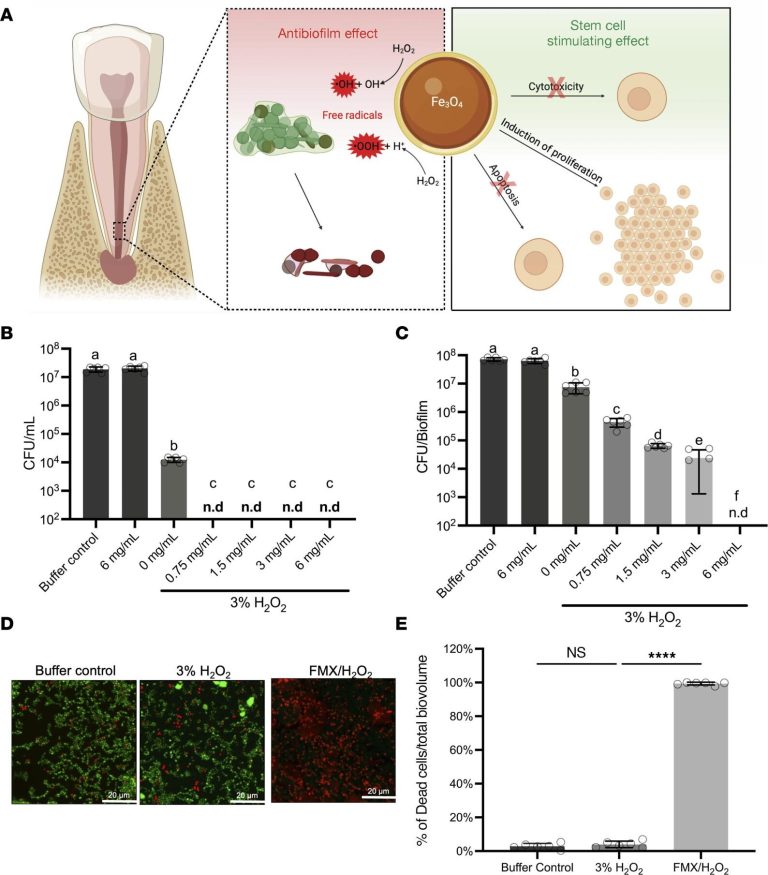
The small size and antimicrobial efficacy of their nanoparticles make excellent candidates for the treatment of biofilm, and the researchers were able to prove that the local applications of zeroxytol in combination with hydrogen peroxide (h (h (h2THE2) Dynamically disturbed biofilm in multiple experimental models.

Clinical efficiency of FMX/h2THE2. Credit: Newspaper of clinical research (2024). DOI: 10.1172/JCI183576
“Ferumoxytol nanoses-because their unique catalytic (enzymatic) activity-are offering new and very effective ways to treat biofilm infections,” says David Cormode of Penn Medicine and Penn Engineering.
“They represent a fascinating new type of therapeutic factor, since they have new therapeutic effects and are low -cost and a fixed shelf.”
Currently, sodium hypochlorite (Naocl) is the solution of gold standard disinfection used during the radical channels. However, it can cause complications if not contained in the treatment area, explains Penn Dental Medicine’s Bekir Karabucak.
“Effective disinfection of the channel’s roots is essential for the success of treatment, however, the targeting of germs while maintaining the maintenance of teeth structure, current procedures require mechanical methods and hard disinfectants to eliminate infection, Karabucak.
Researchers treated 44 patients with peasant periodontitis either with peromoxytol/or2THE2saline or Naocl after undergoing standard endodontic surgeries. The bacterial samples were taken before and after treatment. Found that patients receiving Ferumoxytol/h2THE2 It achieved 99.9% of bacterial measurements without experiencing any adverse effects, proving that this treatment is a safer and effective alternative to Naocl.
As part of their process, they found an unexpected result: the nanomas had a positive effect on a population of stem cells found on the edge of the growing tooth root, stimulating their growth and activating them to produce a bone property.
“What began as a simple research on the possibility of toxicity has evolved into something revolutionary: a treatment capable of eliminating persistent biofilm, while at the same time regenerating the tissue for treatment, which is a new concept for tissue regeneration through the activation of Penn’s tissue cells.”
This finding paves the way for investigating the use of Ferumoxytol nanizlers in vital pulp therapy, a viable alternative to the early stages of the disease that prevents patients from going through the treatment of radical canals.
“Enhancing the success of vital pulp with affordable, effective organic materials can reduce dental care costs. The most important thing is that it helps patients maintain their natural teeth structure and lifelong chewing,” says Karabucak.
Nanoses can also be a very promising approach to repair craniofacial bone abnormalities and the treatment of other bone -related diseases such as osteoporosis, periodontitis and osteopenia caused by autoimmune, given their ability to promote the growth.
Koo is excited about the possibilities.
“Iron oxide nanommiums can be a transformative new category of therapeutic that provides both antibiofilm and regenerative tissue properties, offering a regenerative approach to antimicrobial therapy,” he says. “The options are unlimited: it is biocompatible, cheap for construction and can be incorporated into various compositions. Expanding the use of nanizy to other aspects of oral health care.”
More information:
Alaa Babeer et al, FerumoxyTol nannicles effectively target chronic biofilm infections in top periodontitis, Newspaper of clinical research (2024). DOI: 10.1172/JCI183576
Reference: Nanoparticles offer enhanced treatment for root infection with fewer complications (2025, 24 February) recovered March 125 from
This document is subject to copyright rights. In addition to any fair treatment for private study or research, no part can be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided only for information purposes.